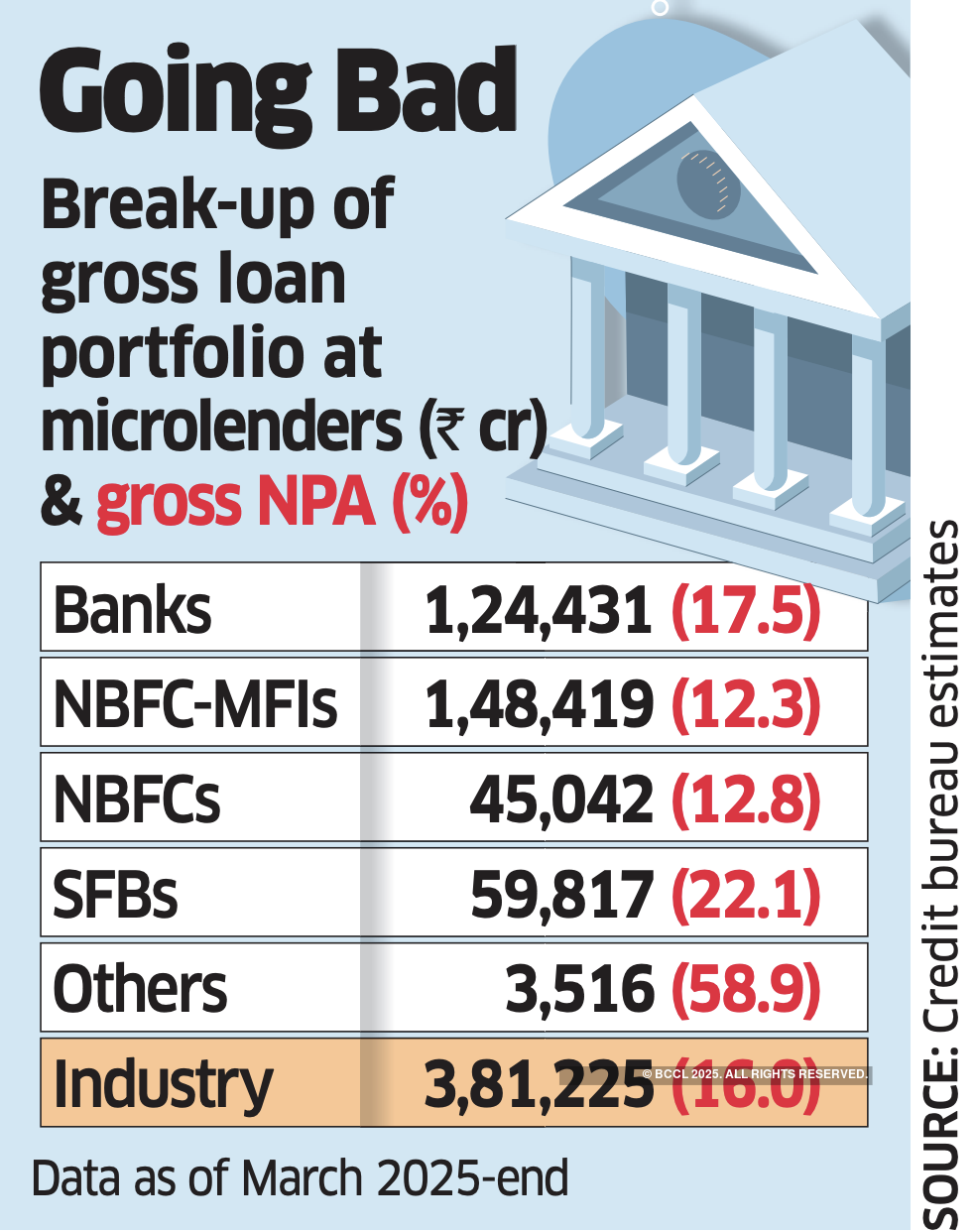
Kolkata: India’s microfinance crisis has deepened with delinquency rates almost doubling. The gross non-performing asset (NPA) ratio for the sector jumped to 16% at the end of FY25 from 8.8% in the year before, with the joint liability-based lending model appearing to be crumbling.
In absolute terms, NPAs spiralled to ₹61,000 crore at March-end from ₹38,000 crore a year ago, said people aware of the matter, citing data compiled by a credit bureau.
Lenders Shrink Books
Over this period, the sector’s cumulative gross loan portfolio contracted about 7% as lenders shrank books in response to rising loan losses.
Among the cross-section of profit-seeking microfinance lenders, the sticky loan ratio was the highest for the small finance bank segment with 22% of its cumulative ₹59,817 crore microfinance loans turning bad at the end of the last fiscal year. For universal banks, the ratio was 17.5% of their ₹1.24 lakh crore of microfinance exposure.
“The recovery is still at a distance. We may see certain green shoots only by the end of FY26. The asset quality stress may prolong for another two-three quarters,” said Shweta Daptardar, vice president, diversified financials, Elara Securities.
The bad loan ratio for the non-banking finance company-microfinance institutions (NBFC-MFI) group was 12.3% and that of other NBFCs was 12.8%.
With Tamil Nadu planning to regulate microfinance operations in the state, the delinquency rate may rise as seen in the case of Karnataka when it enacted a similar law in late February, people tracking the sector said. “The Tamil Nadu Ordinance will exacerbate the challenge further. The Karnataka market took about two months to settle down after the enactment of the microfinance regulation law. Like in Karnataka, the Tamil Nadu bill is also targeted at unregulated entities but it would destabilise the market for some time,” Daptardar said. The sectoral stress has wiped out investors’ wealth significantly with lenders like Fusion Finance and Spandana Sphoorty Financial witnessing about a 66-68% decline in share prices over the past 12 months. CreditAccess Grameen, the country’s largest NBFC-MFI, saw its market value drop 23%. Among high street lenders, IDFC Bank saw its price fall 18% largely on account of the stress in its unsecured portfolio. Microfinance institutions give collateral-free loans to low-income households with annual incomes of less than ₹3 lakh. Women are the primary beneficiaries of such loans. The lenders used to form joint liability groups (JLG) of women that used to act as an intangible collateral for such otherwise unsecured lending.